前言
旨在使用新学的foundry来复现,提升自身水平,以及加强对工具的使用,比赛环境没了,只能自己模拟。
代码仓库:链接
0x00-hello
1. request
使Setup合约中的isSolved函数返回
true。
2. analysis
签到题,很简单,不必多说。
3. solve
攻击合约
1 | // SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT |
0x01-secure
1. request
使得address(setup)合约的WETH代币==50ether。
2. analysis
分析setup合约构造函数的逻辑,
2
3
4
5
WETH.deposit.value(msg.value)(); // address(this)往WETH存了50 ether
WETH.approve(address(wallet), uint(-1)); // 授权 wallet type(uint256).max
// TokenModule(0x00).deposit.selector 等效于 TokenModule.deposit.selector
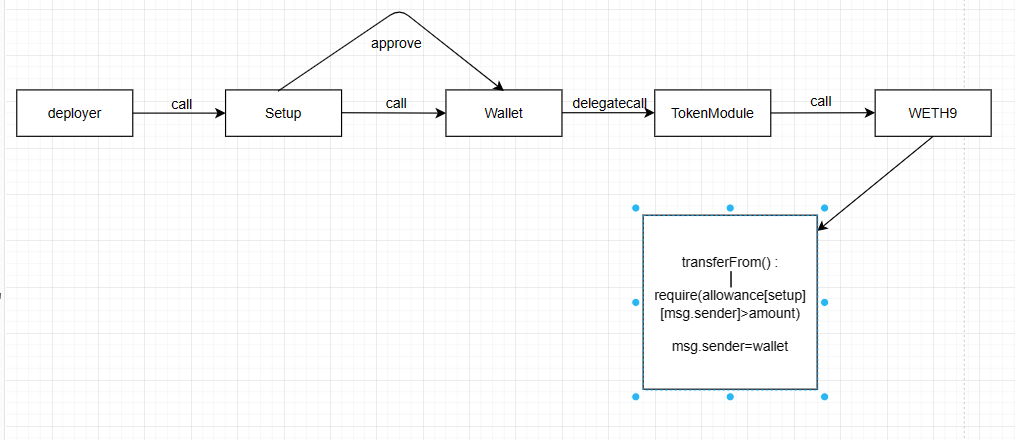
wallet.execModule(tokenModule, abi.encodeWithSelector(TokenModule(0x00).deposit.selector, WETH, address(this), msg.value));因为没有了比赛环境,复现起来有点困难。emmm,大概的意思是:Setup往WETH9中存入了50 ether,并且Setup给Wallet授权使其能够操作Setup的所有WETH代币,然后最后一句就是Wallet将Setup的50 ether WETH代币,全部存入了TokenModule中,此时的
WETH.balanceOf(address(this)) == 0.
WETH.approve(address(wallet), uint(-1))这一步很神奇,直接使得WETH9中的transferFrom函数可以顺利执行(在delegatecall和call的传递链如下)。
TokenModule的withdraw函数没有限制,可以直接取出来,但是无法获取setup中的TokenModule,行不通。网上看一些题解,说挑战者拥有5000ether😓😓😓,那还想那么多干嘛,直接自己存50ether WETH,再转给Setup就ok了。。。解题方式有点出乎意料,复现过程只能自己实现WETH9合约了。
3. solve
攻击合约
1 | // SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT |
0x02-babycrypto
1. request
这是一道python题,先跳过。
2. analysis
首先需要将python的版本降低,否则无法下载sha3库,我这里下载的python3.6,且pip的版本为 10.0.1。
3. solve
以后技术上来了,再回来看看
0x03-broker
1. request
将Broker合约中的WETH代币取出20-25 ether,使得Broker合约的WETH余额小于5 ether。
2. analysis
这道题,emmmm,我不理解的是,我可以拥有WETH 5000 ether,AWT 无限量,但是Token的地址是随机生成的,ta的数值可以比WETH的地址的数值大,亦可以比ta小,所以不同排序方式做题也会不一样,难搞。。。
这道题假定AWT为reverse0,WETH为reverse1。
初步分析:
我手中拥有 5000 ETH,即可以换成 5000 WETH,看到Token合约中的
airdrop函数,这个函数有一个明显的漏洞(可以从该函数中获取无数的token,实现方式是:拥有很多账户)。此时可以将各个合约的token和WETH的数目列出:
contract Token balance WETH balance Setup 0 0 Broker 500_000 ether 25 ether Pair 500_000 ether 25 ether Hacker too much 5000 ether
rate的值是可以由我控制的,因为我手中有着众多的WETH 和 Token,我可以控制汇率!!!该题的题眼在于
liquidata(address,uint256)函数中,只要使得collateralValueRepaid的值处于(20 ether,25 ether)范围即可。这便需要将rate()的值压小,即将其中的reverse0升值,reverse1贬值(在V2中要维持K值恒定,balance0Adjusted.mul(balance1Adjusted) >= uint(_reserve0).mul(_reserve1).mul(1000**2),rate = reverse0 / reverse1,将reverse0的数量减少即升值,将reverse1的数量增多即贬值)。现在的问题是怎么凑这个
collateralValueRepaid,初始的pair的滑点k=500000*25=1.25*10^7,将collateralValueRepaid用表达式表示为:collateralValueRepaid=amount*reverse1/reverse0,我的处理方式为:存入4975 WETH,换出450 000 AWT,此时的滑点为k=5000*50000=2.5*10^8满足swap的条件,liquidate::amount,amount=23 ether * broker.rate(),因为debt[broker]=250_000 ether,所以满足safeDebt(user) <= debt[user] && debt[user] - amount >= 0。综上,攻击思路为:
- 获取30 ether AWT
- 兑换 4975 ether WETH,并存入pair中
- 通过swap函数,兑换出450000 ether AWT
- 给broker授权,再通过liquidate取出 23 ether WETH
没有比赛环境,要复现还是有点困难的,就不去部署V2相关合约了
3. solve
攻击合约
1 | // SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT |
0x04-babysandbox
1. request
使得sandbox合约的代码为0,即毁掉sandbox合约。
2. analysis
BabySandbox中只有一个run函数,分析run函数:
函数体中有三个调用,分别是
delegatecall, staticcall, call,将这三个调用翻译为熟悉的solidity语言为
2
3
4
5
6
address(this).staticcall(msg.data);
address(this).call(msg.data);
// 这里的msg.data 已经被如下操作拷贝到memory [0x00 - calldatasize-1]的位置去了
calldatacopy(0x00, 0x00, calldatasize()) // 将msg.data从0x00的位置拷贝到memory0x00的位置显然,要使得该合约自毁,只能通过delegatecall,而且这是一个空调用,所以自毁逻辑需要在code的fallback中。并且delegatecall的调用者必须是本合约自己,所以只能通过后面的staticall和call来调用,但是涉及了修改合约的状态,所以只能通过call。因此,需要保证staticcall调用成功(且不修改合约变量),call调用成功(修改合约变量),ta们都会再次调用自身的run函数,执行delegatecall,这就需要确保,调用code的两次fallback达成两种不同的效果了(第一次调用不改变变量,即deletecall成功执行,return,跳出staticcall合约调用栈;第二次执行自毁逻辑,即deletecall成功执行,return,跳出call合约调用栈,有点类似ethernaut的elevator)。
这里提供了两种解题方法,一种是通过冷热地址消耗的gas实现,一种是通过
try...catch语句块来实现。(注意第二种方法,因为每一个调用都有gasLimit–0x4000,所以需要逻辑不能太复杂,而且还需要事先将
this记录下来,这是我第一次遇到,可能是减少gas的消耗吧。)
3. solve
验证攻击合约
1 | pragma solidity 0.7.0; |
攻击合约
1 | // hacker1 |
0x05-bouncer
1. request
将bouncer的balance掏空。
2. analysis
这道题的漏洞在于 for循环中复用
msg.value。一开始setup往bouner中存放了52ether。
分析bouncer合约:
合约中涉及到转账(ETH)的只有两个函数
claimFees() payout(), 因为不是owner,所以无法直接执行clainFees函数,也不能通过hatch函数进行插槽覆盖,只能通过payout函数。payount => redeem => covert。想要通过payout取钱,只能调用redeem函数,而tokens mapping只有在convert函数中可以赋值,取钱的前提是token必须是address(ETH),而且ETH和以太的汇率为1:1,所以要是通过convert函数换,只能支付多少换多少WETH。再看到convertMany函数,循环调用convert,这里很明显,只支付一次Entry.amount的费用,便可以兑换ids.length次。综上,攻击思路为
- hacker往bouncer存入8给Entry{amount:10ether,token=ETH}(此时bouncer’s balance=60ether)
- 构建长度为7的ids
- hacker调用convertMany并支付10ether(和Entry.amount相等,此时bouncer’s balance=70ether),convertMany函数体中进行7次兑换,此时
tokens[hacker]][ETH]==70 ether。- 通过redeem函数一次性将bouncer的余额(70ether)全部掏空。
3. solve
攻击合约(enter和convertMany不能在同一个函数中执行,需要拆分,foundry中使用cheatcode改变block.number)。
1 | // SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT |
攻击合约测试
1 | // SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT |
0x06-farmer
1. request
faucet的COMP余额为0,farmer的COMP余额为0,farmer的DAI余额小于expectedBalance。
2. analysis
从isSolve()函数中可以追溯到
CompFaucet,CompDaiFarmer合约,可以看到,
ComFaucet::claimComp()函数可以被人任何人调用,所以可以直接调用该函数使得faucet的COMP余额为0(将所有的COMP转移给了Farmer)。CompDaiFarmer::recycle()函数则是将合约中所有COMP兑换成dai,兑换之后,farmer的COMP余额为0。所以题目的前两个要求可以满足,此时需要想办法使得DAI.balanceOf(address(farmer)) < expectedBalance,看到expectedBalance的计算方式:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
// peekYield()
function peekYield() public view returns (uint256) {
uint256 claimableAmount = IComptroller(comptroller).claimableComp();
address[] memory path = new address[](3);
path[0] = address(COMP);
path[1] = address(WETH);
path[2] = address(dai);
uint256[] memory amounts = router.getAmountsOut(claimableAmount, path);
return amounts[2];
}可以知道:
farmer.peekYield()=COMP=>WETH=>dai。分析各合约的代币:
contract COMP WETH dai setup faucet WETH(50)=>COMP farmer equal comp.balance(faucet) COMP=>WETH=>dai hacker WETH=>COMP 5000 WETH=>dai 题目中的expectedBalance的值实际上是根据当时的pool价格、汇率求出来的;而在v2 pool中代币的价格和代币间的汇率是可以被操控的,前提是维持滑点 K 不变即可。
分析汇率变化对
expectedBalance值的影响:
- dai贬值:DAI.balanceOf(address(farmer)) > expectedBalance
- dai升值:DAI.balanceOf(address(farmer)) < expectedBalance,这正是题目的要求,所以问题转化为如何使dai升值。
代币 (COMP,WETH) (WETH,dai) COMP COMP数量增多,COMP贬值,WETH升值 WETH WETH数量增多,WETH贬值,COMP升值 WETH数量增多,WETH贬值,dai升值 dai dai数量增多,dai贬值,WETH升值 我手中有
5000 ether WETH,我能够影响到comp,weth,weth,dai这里两个交易池。在COMP=>WETH=>dai的兑换路径中,可以事先用手中的WETH在weth,dai交易池中换出dai,此时dai升值,COMP=>WETH=>dai换出的dai便会小于预期。这是典型的 DeFi Sandwich Attacks(三明治攻击)。
3. solve
攻击合约
1 | // SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT |
0x07-yield_aggregator
1. request
将aggregator和bank的WETH代币掏空。
初始状态为:
weth.balanceOf(address(aggregator)) == 0 ether,
weth.balanceOf(address(bank)) == 50 ether
2. analysis
分析 MiniBank合约
该合约很简单,一个铸币一个销币函数,铸币的条件是需要支付等额的WETH代币才可以使得银行balance增加等同的数额,销币则是需要银行余额大于或等于销币数额才可以成功,并向调用者转入等额的WETH代币。
分析 YieldAggregator 合约
该合约两个函数,deposit和withdraw。
deposit函数类似一个交换平台,负责将token代币转换为银行余额(该转换平台,只能转换WETH代币,其他代币无法转,因为该合约的WETH代币数量初始化为0,转换其他代币函数也不会报错)。
withdraw函数负责,从bank中取出WETH,再归还等额的token给msg.sender。不过前提是,msg.sender的poolTokens有足够多的数额。
综上,能取出WETH代币的,只有
burn() 和 withdraw()函数。看到poolTokens的赋值方式:
2
3
4
5
// .....
uint256 balanceAfter = protocol.balanceUnderlying();
uint256 diff = balanceAfter - balanceBefore;
poolTokens[msg.sender] += diff;diff的值由bank的WETH代币数量变动确定,而函数体中的token可以自定义,所以关于token的函数调用中存在了很多执行恶意操作空间,即transferFrom和approve函数中可以自定义函数逻辑。只需要在transferFrom函数中,执行bank.mint() 这样一来既可以使bank的余额增加,也可以使poolTokens[hacker]的值增加,即存一份WETH可以取出两倍的WETH。(事先买好WETH【挑战者拥有5000 ether】,再对bank进行授权操作)
3. solve
攻击合约
1 | // SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT |
攻击合约测试
1 | // SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT |
0x08-market
1. request
将Market合约的balance掏空,初始Market的balance=50ether。
2. analysis
先分析EternalStorage合约
这个合约在fallback函数中,通过汇编实现了
EternalStorageAPI的所有函数,根据fallback中的逻辑,可以将EternalStorage合约的属性抽象出来,如下:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
address owner;
address pendingOwner;
// 类似一个mapping
mapping(bytes32 => TokenInfo) tokens;
struct TokenInfo {
bytes32 name; // 0
bytes32 owner; // 0 + 1
bytes32 approval; // 0 + 2
bytes32 metadata; // 0 + 3
}
}接着分析CryptoCollectiblesMarket合约
能从该合约取出 ETH 的只有sellCollectible()函数(withdrawFee()该函数无法被调用),解题关键肯定是存少取多。该函数要求tokenPrices[tokenId]>0,所以只能通过mintCollectible()函数赋值,而且要求调用者为代币的所有者,该market被代币所有者授权。
话不多说,直接说重点。
可以注意到,在TokenInfo结构体中有一个
metadata属性,这个属性很关键。可以知道每个tokenId的所在的位置为:slot tokenId + 0 = name, slot tokenId + 1 = owner, slot tokenId + 2 = approval, slot tokenId + 3 = metadata。分析铸币之后tokenId对应结构体的变化:
2
3
4
5
6
// slot = tokenId
+ 0 (name): "My First Collectible",
+ 1 (owner): owner
+ 2 (approval):
+ 3 (metadata):将手中的tokenId卖给market,该结构属性的变化:
要卖给market之前需要通过token的approve函数给market授权。
2
3
4
5
6
// slot = tokenId
+ 0 (name): "My First Collectible",
+ 1 (owner): market
+ 2 (approval): 0
+ 3 (metadata):那么要如何实现”存一次钱取多次呢”?
通过
updateName(bytes32,bytes32)将刚刚卖出的tokenId给自己授权1.1 调用该函数的前提要通过
ensureTokenOwner(tokenId),而在ensureTokenOwner(tokenId)函数中,检验的方法便是eq(caller(), sload(add(tokenId, 1))),要求调用者caller,要和sload(add(tokenId, 1))该位置(approval)的值相等,如果在调用updateName函数的使用,传入的tokenId为tokenId+2那么会有一个很神奇的地方,ensureTokenOwner(tokenId)判断的位置为caller和sload(add(add(tokenId, 2), 1))该位置(metadata)的值相等。1.2 所以重点来了!!!只要在铸币之后,卖币之前将
metadata部分的值设为hacker自己,那么每次都要通过updataName(tokenId+2, hacker),使approval的值,由0变成hacker。1.3 此时就可以实现将卖出的币不通过market完成给自己授权的操作。
再看到Market的
transferFrom函数,该函数的功能是将代币的所有权转移给某个账户,前提:该代币的所有者必须给调用者授权,在上一步中已经知道如何实现,不通过代币所有者直接完成授权操作(前提是实现修改代币的metadata部分)。所以便可以以approval的身份调用该函数成为tokenId的owner。简单计算需要如何将market的balance掏空
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
// 通过 mintCollectibleFor 函数铸币需要被收取 (1 / 11)的手续分
// 那么到账户手中的实际只有 (10 / 11)
/*
计划取两次将钱取完,设铸币量为:x,
有: 50 + x = (10 / 11) * x * 2
化简得: (9 / 11) * x = 50
emmm,很不好算,我喜欢整数,x 取 66,则需要等式右边为54,
这里可以通过自毁合约强行给合约转钱,这样一来就好算了。
*/综上,攻击思路为:
- 通过自毁合约,往market转4ETH;
- 通过
mintCollectible合约获取tokenId(这样才可以修改metadata部分),并转入66 ether;- 修改通过
updateMetadata()修改metadata的值,再通过CryptoCollectibles的approve函数给market授权(为了成功执行sellCollectible()函数)- 调用
sellCollectible()函数,先拿出60ether- 调用
updataName(tokenId+2, hacker),成为代币的被授权者- 调用
CryptoCollectibles.transferFrom(tokenId, market, hacker),再次成为tokenId的所有者- 最后授权market,再次执行
sellCollectible()函数即可。
3. solve
攻击合约
1 | pragma solidity 0.7.0; |
攻击合约测试
1 | // SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT |
0x09-lockbox
1. request
这道题要求将Entrypoint合约中的
solved变量修改为true,即要求成功执行Entrypoint合约中的solve函数。
2. analysis
分析Entrypoint合约可知,这道题是要将
Entrypoint,Stage1,Stage2,Stage3,Stage4,Stage5中的solve函数全部成功执行,而且calldata不变,也就是说使用一次calldata通过所有的solve。而调用的终止条件是
2
3
4
if iszero(next) {
return(0, 0)
}这将会在 Stage5 中满足。
在
Stage5中规定了calldata的长度为 256bytes,所以只能在规定长度的calldata中通过所有“关卡”,慢慢拼凑出calldata。起始calldata为
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 // 0x20
0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 // 0x40
0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 // 0x60
0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 // 0x80
0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 // 0xa0
0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 // 0xc0
0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 // 0xe0接下来逐一过关,拼凑出calldata
- 调用Entrypoint中的solve(bytes4 guess)
- 这个guess很好猜,坏随随机数,可以提前计算;
- (guess从高位截取),此时的calldata为:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
[ guess ]0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 // 0x00
0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 // 0x20
0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 // 0x40
0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 // 0x60
0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 // 0x80
0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 // 0xa0
0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 // 0xc0
00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 // 0xe0
调用Stage1中的 solve(uint8 v, bytes32 r, bytes32 s)
需要拿到
0x7E5F4552091A69125d5DfCb7b8C2659029395Bdf账户的私钥,并对keccak256("stage1")进行签名。注意:
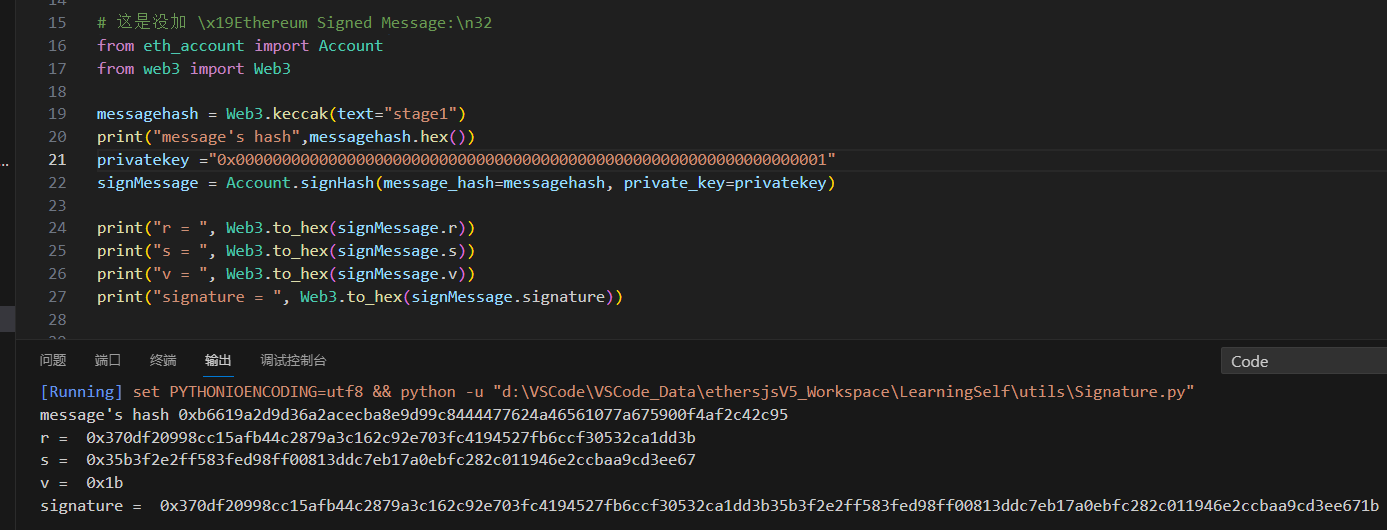
0x7E5F4552091A69125d5DfCb7b8C2659029395Bdf的私钥可以Google查到,私钥就是1,需要使用该私钥对keccak256(“stage1”)进行签名,这里要注意的是,不能采用以太坊的签名方式(即,在消息前加上\x19Ethereum Signed Message:\n32,在这里踩坑很久。。。)使用python脚本计算v,r,s
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
from web3 import Web3
messagehash = Web3.keccak(text="stage1")
print("message's hash",messagehash.hex())
privatekey ="0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001"
signMessage = Account.signHash(message_hash=messagehash, private_key=privatekey)
print("r = ", Web3.to_hex(signMessage.r))
print("s = ", Web3.to_hex(signMessage.s))
print("v = ", Web3.to_hex(signMessage.v))
print("signature = ", Web3.to_hex(signMessage.signature))
- 注意这里的
uint8 v参数从4bytes之后的第一个32bytes中取低 1byte,r在0x20,s在0x40- 此时的calldata为:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
[ guess ]000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001b // 0x00
370df20998cc15afb44c2879a3c162c92e703fc4194527fb6ccf30532ca1dd3b // 0x20 => r
35b3f2e2ff583fed98ff00813ddc7eb17a0ebfc282c011946e2ccbaa9cd3ee67 // 0x40 => s
0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 // 0x60
0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 // 0x80
0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 // 0xa0
0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 // 0xc0
00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 // 0xe0
调用Stage2中的solve(uint16 a, uint16 b)
这里需要使得a和b相加的结果发生上溢,编译器为
0.4,所以要使得溢出很简单,即0x00后2bytes和0x20后2bytes的值相加发生溢出即可,这要求a> =0xFFFF - 0xDD3B = 0x22CC。
- 所以需要修改 0x00 后2bytes的值,将其修改为
0x991B- 所以此时的calldata为
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
[ guess ]000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000991b // 0x00
370df20998cc15afb44c2879a3c162c92e703fc4194527fb6ccf30532ca1dd3b // 0x20 => r
35b3f2e2ff583fed98ff00813ddc7eb17a0ebfc282c011946e2ccbaa9cd3ee67 // 0x40 => s
0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 // 0x60
0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 // 0x80
0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 // 0xa0
0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 // 0xc0
00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 // 0xe0
调用Stage3中的solve(uint idx, uint[4] memory keys, uint[4] memory lock)
4.1 这里要求
keys[idx % 4] == lock[idx % 4],此时的idx的值便是0x00所在位置的值,以0x1B结尾,如果对4去模,取模的结果只能等于3,即idx % 4 = 0,而在Stage5中的solve()限制calldata的长度,我们知道calldata后面全是用0补齐,所以即使我传入的calldata中不包括lock[3],那么EVM会从后面的空闲位置取值,也就是取零,即lock[3]=0。所以,不能让v等于0x1B,如果让v等于0x1C的话,0x1c % 4 = 0,那么这个lock[0]在可控的calldata中。综上可知,求解的签名不对,所以需要重新求出签名。在现如今很多的工具库中,求签名的函数被封装好了的,但是可以去修改源码,更改secp256k1中的临时密钥,可以实现。4.2 这里要求
keys[i] < keys[i + 1],现如今的key[0] < key[1]即r < s,所以生成的签名要求v=28, r < s。4.3 这里要求
(keys[j] - lock[j]) % 2 == 0,这里可以根据keys数组修改lock数组的值,使其的差为二的倍数,且keys[3]的值一定是偶数。通过
ethereumjs计算出符合要求的signature
2
3
4
5
6
7
Message Hash: b6619a2d9d36a2acecba8e9d99c8444477624a46561077a675900f4af2c42c95
Signature: {
v: 28,
r: '219df4f90e49c25326119aebb09876e3ca5d0cbd1e60c23dee1be7a5d87e6b6f',
s: '64ebcb040f8b62a0f2ff148604f36ef756c3558cd54c2d008447e8119f2b45f7'
}此时的calldata为
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
[ guess ]000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000991c // 0x00
219df4f90e49c25326119aebb09876e3ca5d0cbd1e60c23dee1be7a5d87e6b6f // 0x20 => r keys[0]
64ebcb040f8b62a0f2ff148604f36ef756c3558cd54c2d008447e8119f2b45f7 // 0x40 => s keys[1]
e201a979a73f6a2947c212ebbed36f5d85b35629db25dfd9441d562a1c6ca896 // 0x60 keys[2]
e201a979a73f6a2947c212ebbed36f5d85b35629db25dfd9441d562a1c6ca89a // 0x80 keys[3]
219df4f90e49c25326119aebb09876e3ca5d0cbd1e60c23dee1be7a5d87e6b6f // 0xa0 lock[0]
0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003 // 0xc0 lock[1]
00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 // 0xe0 lock[2]调用Stage4中的solve(bytes32[6] choices, uint choice)
要求
choices[choice % 6] == keccak256(abi.encodePacked("choose"),而choice的值对应lock[1]此时lock[1]%6==1,可以将lock[1]修改为3,那么lock[1]%6==3,所以此时的calldata为
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
[ guess ]000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000991c // 0x00
219df4f90e49c25326119aebb09876e3ca5d0cbd1e60c23dee1be7a5d87e6b6f // 0x20 => r keys[0]
64ebcb040f8b62a0f2ff148604f36ef756c3558cd54c2d008447e8119f2b45f7 // 0x40 => s keys[1]
e201a979a73f6a2947c212ebbed36f5d85b35629db25dfd9441d562a1c6ca896 // 0x60 keys[2]
e201a979a73f6a2947c212ebbed36f5d85b35629db25dfd9441d562a1c6ca89a // 0x80 keys[3]
219df4f90e49c25326119aebb09876e3ca5d0cbd1e60c23dee1be7a5d87e6b6f // 0xa0 lock[0]
0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003 // 0xc0 lock[1]
00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 // 0xe0 lock[2]最后还要注意函数调用的方式,要么通过ethersjs发送指定的calldata,要么通过汇编发送指定的calldata。
3. solve
攻击合约
1 | // SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT |
攻击合约测试:
1 | // SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT |
0x0a-bank
1. request
这题要求将bank的WETH代币掏空。
2. analysis
该题中能减少WETH余额的函数只有``withdrawToken()
函数,而执行的逻辑为:首先得有足够的钱,才可以从bank中取出,所以本题的的漏洞可以是通过该函数骗bank的钱。问题进而转变为如何使得mapping(address => uint) balances`该映射的值大于自己实际的存储金额。看到结构体且在低版本中,我首先想到的是利用结构体的插槽覆盖,分析了下该方法不可行,因为
Account storage account都是从映射accounts中取出来的,所以并不会存在插槽覆盖。看到本题涉及了动态数组,且
setAccountName(uint accountId, string name)函数是一个修改动态数组任意索引位置的值的函数。所以可以想办法使accounts数组的长度变为type(uint256),分析可知withdrawToken()和closeLastAccount()函数都涉及了数组长度修改的操作,但是在withdrawToken()中token是自定义的,所以可以进行函数的外部调用,看到如下代码
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
require(accountId < accounts[msg.sender].length, "withdrawToken/bad-account");
require(ERC20Like(token).balanceOf(address(this)) >= amount, "withdrawToken/low-sender-balance");
// if the user has emptied their balance, decrement the number of unique tokens
if (account.balances[token] == 0) {
account.uniqueTokens--;
if (account.uniqueTokens == 0 && accountId == lastAccount) {
accounts[msg.sender].length--;
}
}
}仔细看这就是很明显的重入,先判断数组长度,执行外部调用,最后在更新数组的长度,这里完全可以在执行外部函数调用的时候调用
withdrawToken()函数,从而可以通过``require(accountId < accounts[msg.sender].length, “withdrawToken/bad-account”);`断言。这个balanceOf的重入有点难。。。直接借鉴大佬的:链接
将数组的长度设置为
type(uint256)之后,接下来考虑的是覆盖。
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
accounts_slot = keccak256(abi.encode(msg.sender,0x02));
// 找到`Account[accountId]`的位置
account_slot = keccak256(abi.encodePacked(accounts_slot)) + 3 * accountId;
// 找到第n个Account.balances插槽的位置
balances_slot = account_slot + 3 * accountId + 2;
// 找到第n个Account的WETH对应的余额
weth_slot = keccak256(abi.encode(address(WETH), balances_slot))就极度复杂。。。。。
3. solve
攻击合约
1 | // 先留着吧 |
🤪剩下的题目以后水平上来了再来做~